Happy to see you trying Dataview for the first time! It can be a headache. But, I promise you, its worth it! Nonetheless, It can be a bit tricky
Using Dataview DQL
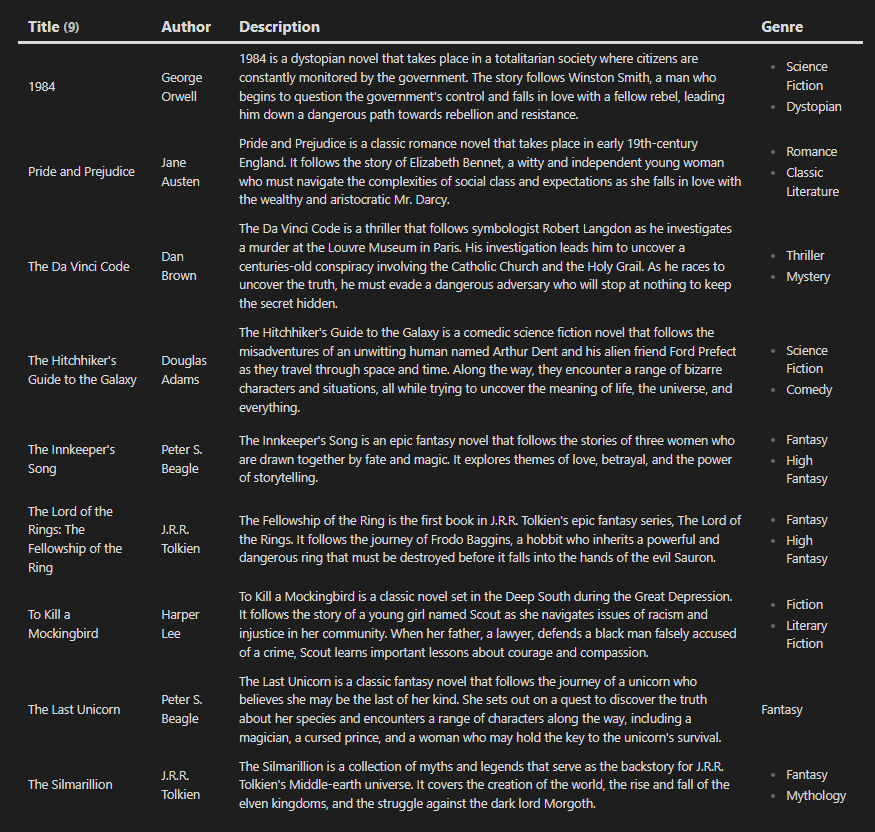
```dataview
TABLE WITHOUT ID file.link AS "Item", name as "name", price as "price", someothervalue as "someothervalue"
FROM "Dataview Test" and #item
```
```dataview
TABLE WITHOUT ID sum(map(rows, (r) => default(r.price, 0))) AS "Total Price"
FROM "Dataview Test"
GROUP BY true
```
Explanation
The first table displays…our table. The second table displays the summary by using GROUP BY to turn all the rows into a singular row that can be added together using sum
Using DataviewJS
let pages = dv
.pages('"Dataview Test" and #item')
let totalPrice = pages.map((page, index) => [
page.file.link,
page.name,
page.someOtherValue,
dv.func.sum(page.price),
]);
totalPrice["values"][totalPrice.length] = [
"***Total***",
"",
"",
dv.func.default(dv.func.sum(pages.price), 0),
];
dv.table(["Item", "Name", "someOtherValue", "Price"], totalPrice);
Explanation
Using @justdoitcc 's script, from,
The script declares the variable pages and uses dv.pages to query all pages that are in the folder “Dataview Test” and have the tag #item
Next, the variable totalPrice is declared and uses pages.map. The map method takes a function as an argument, which is called for each element in the pages array. In this case, the function takes two parameters: page and index.
For each page in the pages array, the function creates an array with four values: page.file.link, page.name, page.someOtherValue, and dv.func.sum(page.price)
page references the individual query results from dv.pages. Using page.file.link we can collect each queries file link. Using page.name we can find its name value (our tag), as well as someOtherValue. Finally, we use dv.func.sum(page.price) to sum all price fields on the page
Afterwards, an array called is created. This array has the values “Total”, two blank values, and dv.func.default(dv.func.sum(pages.price), 0). This array adds predetermined values to totalPrice
dv.func.default(dv.func.sum(pages.price), 0) sums up all price values in all queried pages. It looks very similar to dv.func.sum(page.price) which is why you need to pay extra attention to “page” vs “pages”
Finally, we use dv.table to create four columns to match our array, these columns correspond with the order of the array values. page.file.link was referenced first so it goes with Item, next we have page.name which goes with Name, etc
The totalPrice array is referenced to populate the table
Then…wala! Thats the code explanation
Extra
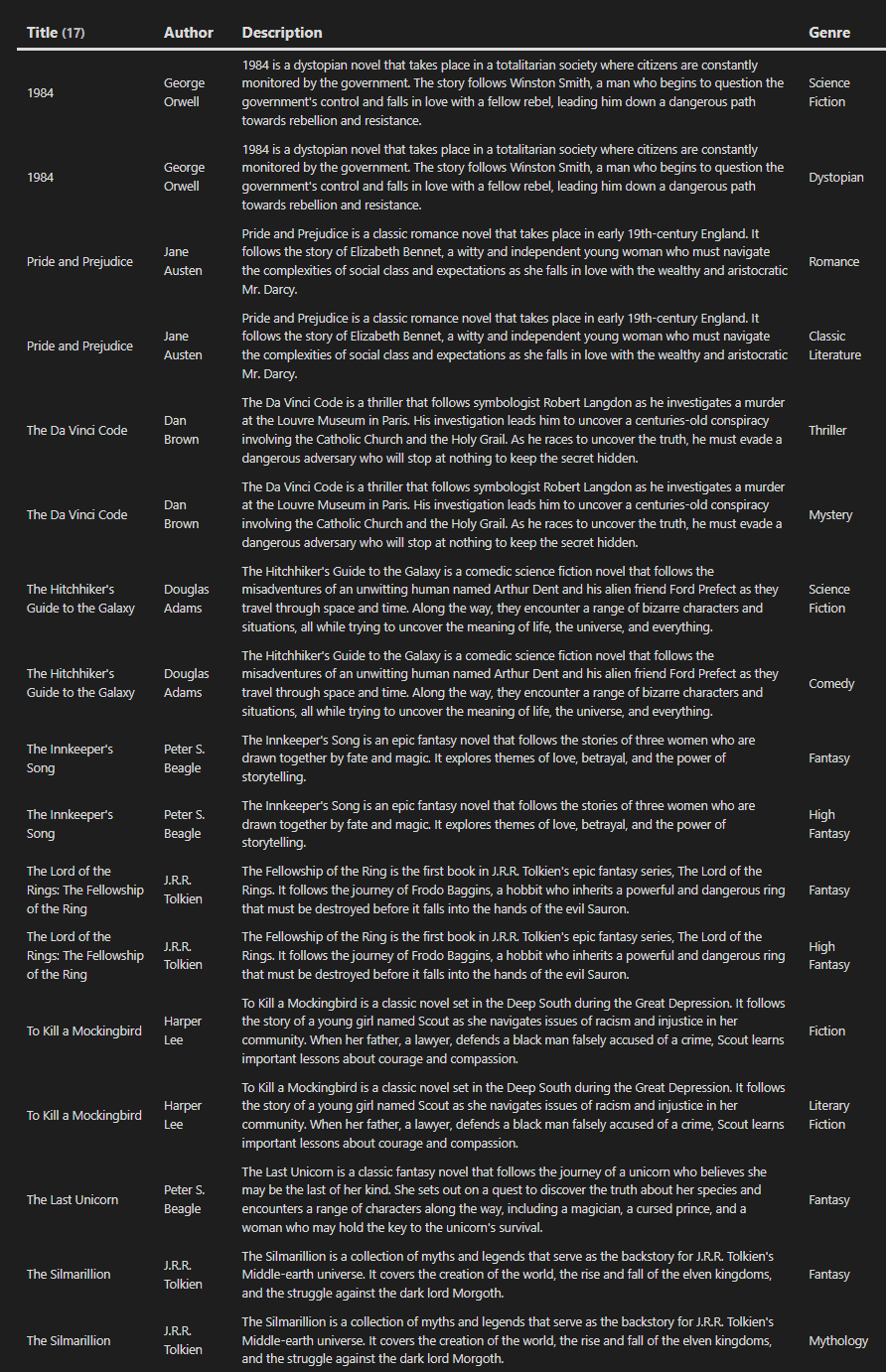
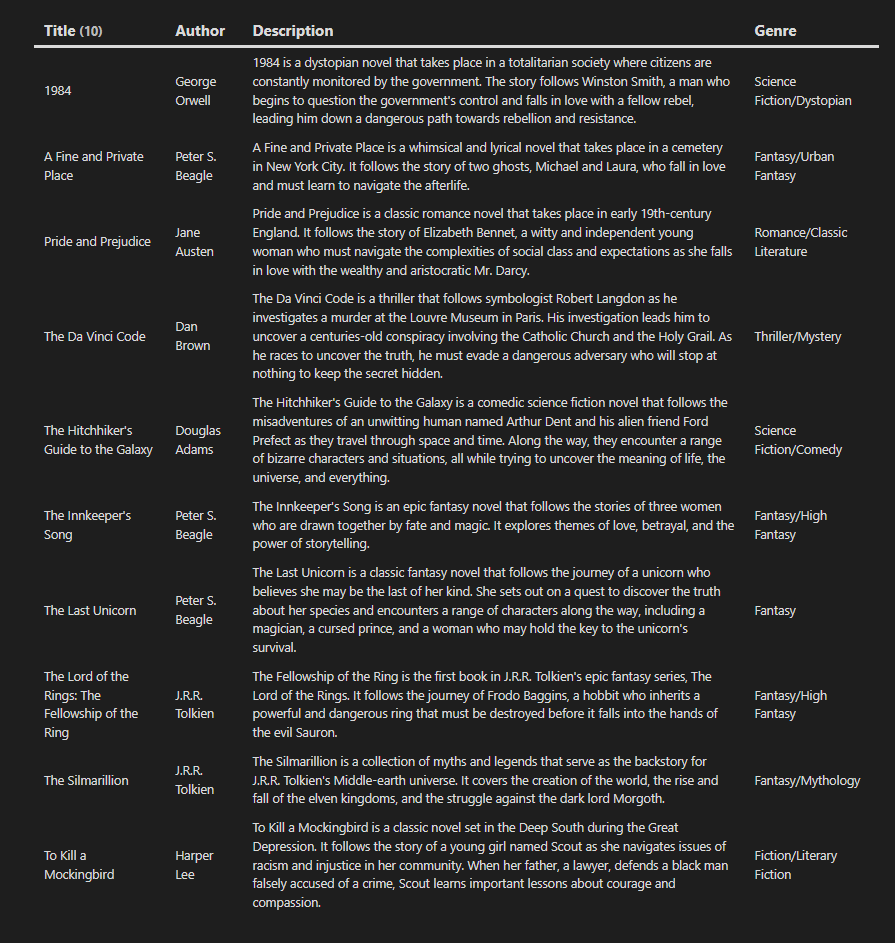
What is FLATTEN?
Essentially, FLATTEN organizes your results by separating them to their own rows. For example, if Object1 have the values of Value1 and Value2, instead of it being listed as Object1, Value1 Value2 it would be Object1 Value1 and Object1 Value2
Here’s an example,
Without Flatten
With Flatten
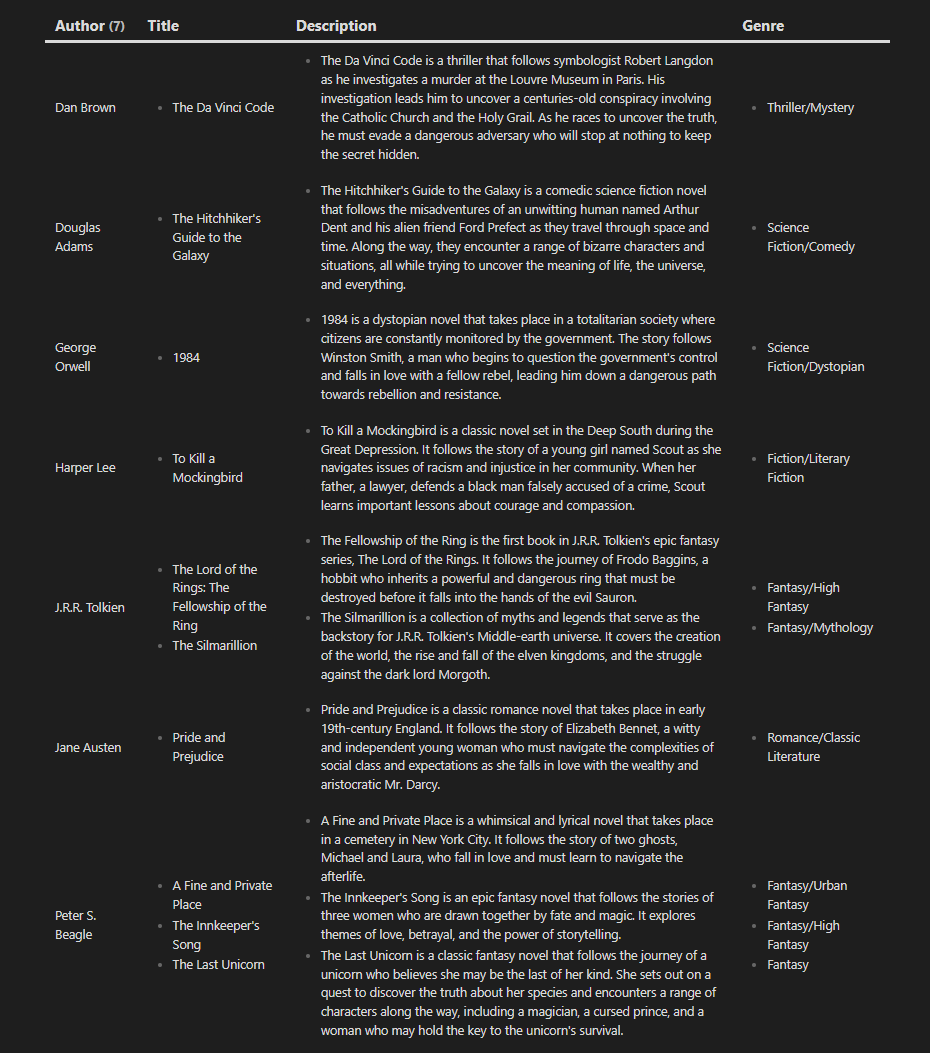
What is GROUP BY?
GROUP BY is the direct opposite of FLATTEN. While FLATTEN separates values, GROUP BY groups them together
Here’s an example,
Without GROUP BY
With GROUP BY